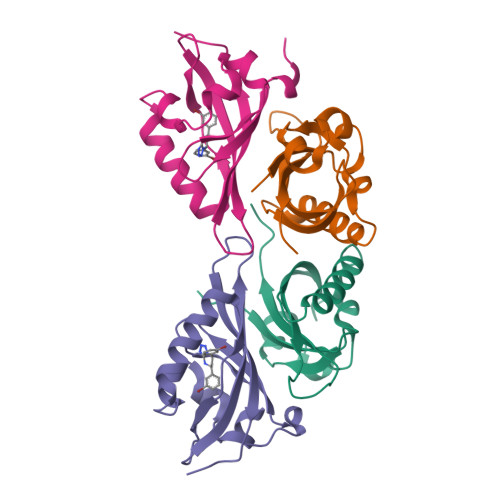
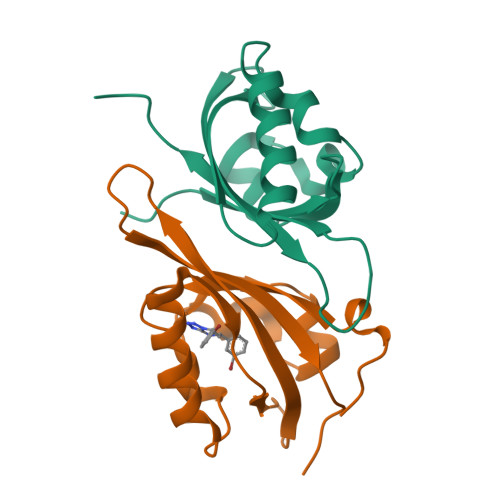
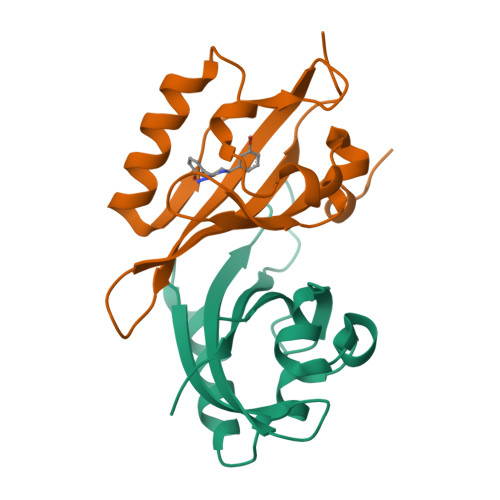
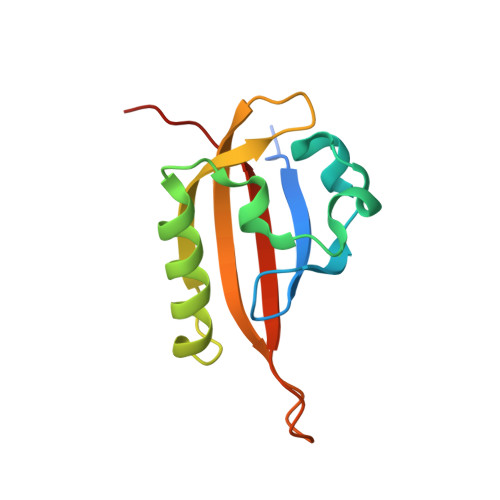
Isoform-Selective and Stereoselective Inhibition of Hypoxia Inducible Factor-2.
Scheuermann, T.H., Stroud, D., Sleet, C.E., Bayeh, L., Shokri, C., Wang, H., Caldwell, C.G., Longgood, J., MacMillan, J.B., Bruick, R.K., Gardner, K.H., Tambar, U.K.(2015) J Med Chem 58: 5930-5941
- PubMed: 26226049
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00529
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4XT2 - PubMed Abstract:
Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) transcription factors reside at the center of signaling pathways used by mammalian cells to sense and respond to low oxygen levels. While essential to maintain oxygen homeostasis, misregulation of HIF protein activity correlates with tumor development and metastasis. To provide artificial routes to target misregulated HIF activity, we identified small molecule antagonists of the HIF-2 transcription factor that bind an internal cavity within the C-terminal PAS domain of the HIF-2α subunit. Here we describe a new class of chiral small molecule ligands that provide the highest affinity binding, the most effective, isoform-selective inhibition of HIF-2 in cells, and trigger the largest protein conformation changes reported to date. The current results further illuminate the molecular mechanism of HIF-2 antagonism and suggest additional routes to develop higher affinity and potency HIF-2 antagonists.
Organizational Affiliation:
†Department of Biophysics, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, 5323 Harry Hines Boulevard, Dallas, Texas 75390, United States.